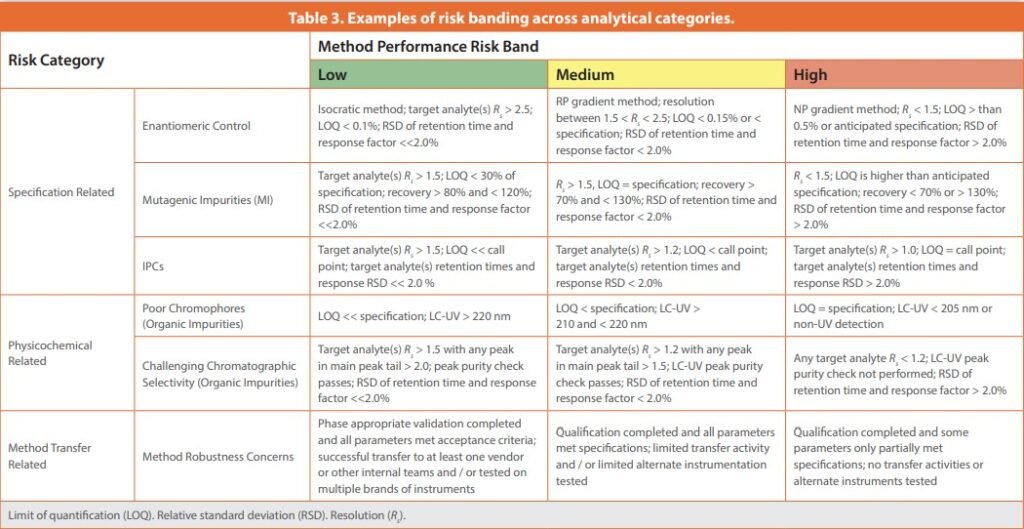
Celgene risk management is a program designed to make sure certain powerful medicines are used safely. It’s especially important in the United States, where strict rules protect patients from potential risks. This guide explains everything about Celgene’s risk management program (REMS), how it works, and what patients, doctors, and pharmacies need to know.
What Does Celgene Risk Management Mean?
Celgene risk management is a system created by Celgene (now part of Bristol Myers Squibb) to help control and monitor the use of certain high-risk medicines. These medicines, like Revlimid (lenalidomide), Pomalyst (pomalidomide), and Thalomid (thalidomide), are highly effective but can cause serious birth defects or other health risks if not used properly.
Because of these risks, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires Celgene to run a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS). This program puts strict guidelines in place for doctors, pharmacists, and patients to follow when using these drugs.
The goal is simple: keep patients safe while still allowing access to life-saving treatments.
Why Is Celgene Risk Management Important?
Celgene risk management is not just a set of rules—it’s a lifeline for patient safety. Medicines like thalidomide have a history of causing birth defects if taken during pregnancy. To avoid repeating past tragedies, Celgene’s REMS program ensures only those who understand the risks and follow all safety steps can access the drugs.
This approach protects unborn babies from exposure and also reduces the risk of misuse, overdose, or other side effects. For cancer patients or those with blood disorders, these drugs can mean the difference between life and death. But they must be used in a controlled and educated way to prevent harm.
By requiring special enrollment, regular testing, and limited distribution, Celgene’s system creates a circle of safety that involves patients, healthcare providers, and pharmacies working together.
How Does Celgene Risk Management Work?
Celgene’s risk management program works through a closed-loop system called REMS. Only certified prescribers and pharmacies can prescribe and dispense the covered medicines. Patients must also enroll and agree to follow strict guidelines.
Each step ensures the medicine is used only by the right patients, at the right time, in the safest way possible. This process requires ongoing monitoring and compliance from all parties involved.
Patient Responsibilities
Patients have a key role in Celgene risk management. Before starting treatment, they must:
- Enroll in the REMS program
- Undergo mandatory counseling about the risks
- Commit to using approved birth control methods if of childbearing potential
- Take regular pregnancy tests as required
- Sign consent forms acknowledging they understand and accept the risks
Patients must also ensure they only receive their medication from certified pharmacies and keep follow-up appointments as scheduled.
Doctor Responsibilities
Prescribers must be certified by Celgene REMS. Their responsibilities include:
- Counseling patients on the risks and safe use of the medication
- Ensuring patients meet all eligibility criteria
- Completing and submitting necessary documentation
- Ordering and reviewing mandatory pregnancy tests
- Reporting any adverse events to Celgene or the FDA
They act as the first line of defense in the risk management process.
Pharmacy’s Role
Pharmacies dispensing these drugs must also be certified. Their role involves:
- Verifying patient enrollment in REMS
- Confirming all safety steps are completed before dispensing
- Keeping accurate records of dispensed medications
- Providing counseling on safe handling and disposal of the drug
This three-way partnership between patients, doctors, and pharmacies creates a secure system for handling these sensitive medicines.
Which Medicines Need Risk Management?
Celgene’s REMS program applies to certain medicines that have serious safety concerns. The most notable ones include:
- Thalomid (thalidomide): Used for multiple myeloma and leprosy-related conditions, but has a history of causing severe birth defects.
- Revlimid (lenalidomide): Another treatment for multiple myeloma with similar risks to thalidomide.
- Pomalyst (pomalidomide): Used in certain blood cancers and also carries teratogenic risks.
All three drugs are available only under strict REMS controls and cannot be purchased over-the-counter or from non-certified sources.
What Is the REMS Program in the USA?
The REMS program (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy) is an FDA-mandated safety system required for certain high-risk drugs. In Celgene’s case, their REMS program focuses on preventing fetal exposure to teratogenic drugs and ensuring patients are fully aware of the potential dangers.
In the U.S., REMS programs like Celgene’s involve certification, education, and monitoring to ensure compliance at every step. This is especially crucial for drugs with a narrow safety margin.
How Can Patients Sign Up for Celgene Risk Programs?
Enrolling in Celgene’s REMS program is mandatory for any patient who needs these medications. The enrollment process is straightforward but requires attention to detail to ensure all safety requirements are met.
Easy Steps to Enroll
- Visit your doctor and discuss whether the medicine is right for you.
- Complete counseling about the risks and safe use.
- Sign consent forms provided by your doctor.
- Undergo a pregnancy test if required.
- Receive confirmation of enrollment from Celgene REMS.
Only after completing these steps can your prescription be filled.
Documents You May Need
To enroll, patients may need:
- Government-issued photo ID
- Health insurance information (if applicable)
- Signed patient agreement/consent form
- Recent pregnancy test results (if of childbearing potential)
About Celgene Risk Management
Celgene’s REMS isn’t just paperwork—it’s a patient safety shield. The program empowers patients with knowledge and makes sure medicines are used correctly, minimizing risk while maximizing benefits.
Thoughts on Celgene Risk Management
Celgene risk management is a perfect example of how drug safety and patient care can go hand in hand. While the process may seem strict or even inconvenient, it exists for a good reason: to save lives and prevent harm. Patients and healthcare providers who understand and embrace the system can use these powerful therapies with confidence.
The Bottom Line
Celgene risk management is not optional—it’s essential. It protects patients, prevents tragedies, and ensures that life-changing treatments are used safely. For anyone prescribed Thalomid, Revlimid, or Pomalyst, enrolling in and following the REMS program is the only way to access these drugs legally and safely in the United States.
By working together—patients, doctors, and pharmacies—this system keeps everyone safer and supports better health outcomes.